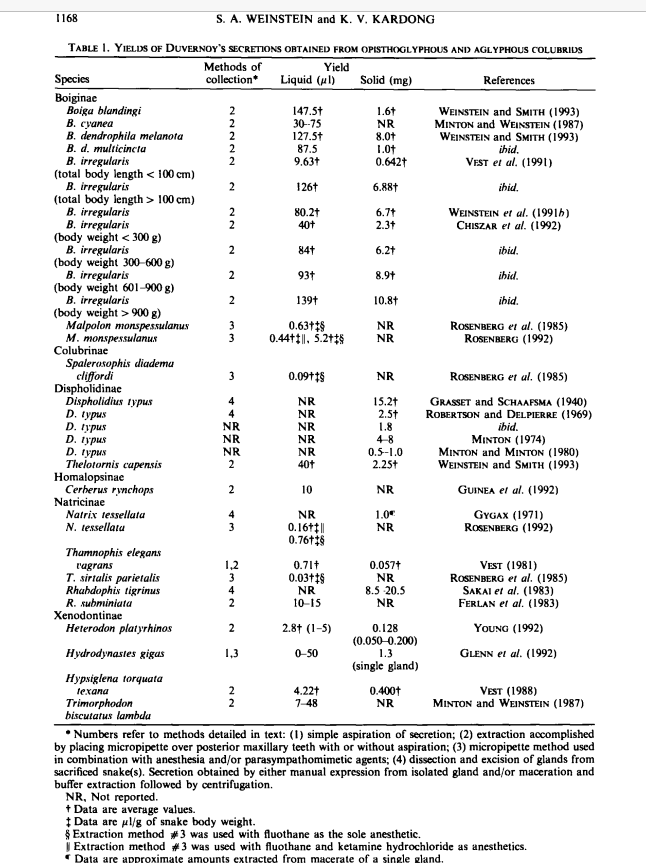
Properties of Duvernoys Secretions from opisthoglyphous and aglyphous colubrid snakes – Weinstein & Kardong, 1994
Extraction of duvernoys secretions: methods, yields and storage:
The normal milking technique is not suitable for snakes with rear fangs and duvernoys glands that have weak venom release systems. Also electrical stimulation doesn’t work well given their altered muscle structure surrounding the organ. Four main methods are used for to collect venom secretions/mixed oral secretions from colubrids.
- Washing Oral Membranes:
This method mainly involves using a disposable micropipette attached to a tube connected to a flask that facilitates aspiration via a vacuum sourced to the flask. The micropipette is then moved along the oral regions of the snake including different tooth rows and saliva can be further stimulated with light use of distilled water. The sample is then collected in a test tube, frozen and lyophilized (freeze-dried) and stored in a dark at -30 to -70 celsius. This method works best for snakes that are aglyphous, I think hognoses are cause they also have backward facing grooved teeth, and produce small amounts of venom. The issue with this method is that different organs secrete into the oral region of the snake which can mean a mixture of compounds. - Directly From Enlarged Tooth:
If the snake’s grooved teeth are visible then secretions can be collected via 100-200 microlitre pipettes/tooth or much smaller pipettes depending on the snake’s teeth. A vacuum aspiration can be used or not, and after placing the pipette the secretions should start flowing into the pipette naturally. This method is tedious and slow, and some snakes may try to bite onto the pipette which can break the pipette or damage the snake or introduce blood/other chemicals into the solution. If done correctly it can collect very precise samples of specific oral regions in the snake. The samples are then stored over desiccant at the same conditions and methods as stated previously. I think the snakes are not anesthetized but rather just manually restrained, which could affect our study since we want to minimize the stress of manual milking. - Pipette and parasympathomimetic stimulation:
This is the whole ketamine followed by pilocarpine method, basically knock the snake out and then introduce a chemical that encourage salivation. This makes collecting the secretions very easy and increases the amount collected. However the issue with this is that identifying the correct dose of anesthesia is hard so it could kill the snake. Using different anesthesia may affect the secretion components like proteins, and in snakes it is unclear whether using chemicals to stimulate gland activation affects the composition. A rodent study showed that it did not. Also repeatedly using this method may harm the captive snakes over a long-term period. Check out previous posts on this site to check out the more in depth explanation of this method or check out the paper. - Gland maceration:
This is also a method that is discussed in previous posts, it includes carefully dissecting the required organs from sacrificed individuals. The best way to do this is making cuts to the ducts that lead to the gland to prevent it from leaking. After removal it can be kept on ice and kneaded or extracted via syringe, or it can be macerated as a whole organ in a cold homogenizer encased in an ice bucket and extracted with physiological saline (check paper for specifics). After centrifuging, the sample can be filtered and stored at -30 to -70 celsius. The drawbacks with this is that the maceration sample will have components that normal venom won’t because the entire organ is present, but it gives a large sample to use and compare. This study also mentions the use of polyether foam or a membrane that the snakes bite onto then the apparatus is squeezed/pipetted or washed and pooled together to make a sample. The sample can be lyophilized and frozen but it doesn’t produce high volumes.
- This paper mentions a study that used the directly from tooth method with hognose snakes. Also check paper for analysis methods.